Based on the fanning effect self-pumped and mutually pumped phase
conjugation is demonstrated in photorefractive BTO-crystals with
applied electric ac-fields. Experimental results are given characterizing
the spatial and temporal behavior of the phase conjugated wave.
Phase-conjugation (PC) can be realized using Four-Wave Mixing (FWM) in photorefractive crystals.
Two waves (signal and pump) create a hologram inside the medium which is read out by a second pump wave.
The fanning (unisotropic amplified scattered light) found in photorefractive materials with strong coupling can provide self-aligning pump waves.
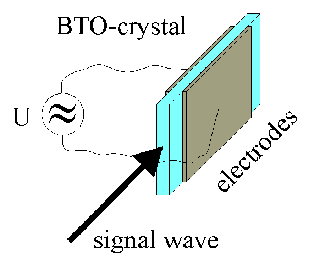
Until now such fanning is found only in few materials (e.g. BaTiO3). Application of an ac-electric field enhances the gain in crystals of the sillenite type like Bi12TiO20 (BTO). Fiber-like crystals (see fig.) provide a long interaction area and a small electrode distance ( high electric field (and strong enhancement) with moderate voltages).

M. Esselbach, G. Cedilnik, V. Prokofiev, A. Kiessling, and
R. Kowarschik
We use the resulting fanning with a square-wave electric field for 3 types of phase-conjugators where the readout wave is given by:
We present results showing the satisfactory quality of the PC-process with regard to the transmission of intensity and phase structures to the PC-wave. The temporal behavior of the PC-wave shows the initial buildup, the reaction on transient intensity and phase patterns, and the strong influence of the time dependent electric field.